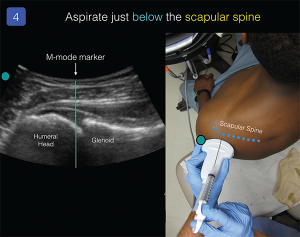
3. Aspirate the glenohumeral joint.
Explore This Issue
ACEP Now: Vol 35 – No 06 – June 2016I recommend standard sterile precautions for all joint aspirations (sterile probe cover, sterile gloves, etc.). Use the M-mode marker to center the transducer over the space between the glenoid fossa and humeral head. Place a small anesthetic skin wheal at this location. With an 18–21 g, 3.5-inch spinal needle attached to a control syringe, advance the needle tip just parallel to the probe, just under the scapular spine (see Figure 4). The out-of-plane technique does not allow for clear needle visualization but offers a simplified method to enter the glenohumeral joint capsule. While advancing the needle, gently aspirate until synovial fluid is obtained.
Summary
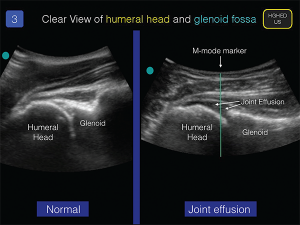
Clinicians should be familiar with a simplified method for the ultrasonographic evaluation of the glenohumeral joint. The presence of a joint effusion on point-of-care ultrasound evaluation in the correct clinical setting will indicate the need for joint aspiration and fluid analysis. The out-of-plane posterior approach to glenohumeral aspiration allows for a simplified method for a safe and efficacious joint aspiration.
Contributors
Dennis Hsieh, MD, JD, Resident Physician, Highland General Hospital, Alameda Health System
Marcus Williams, MD, Resident Physician, Highland General Hospital, Alameda Health System
Daniel Mantuani, MD, MPH, Attending Physician, Assistant Director, Emergency Ultrasound, Highland General Hospital, Alameda Health System
Arun Nagdev, MD, Attending Physician, Director, Emergency Ultrasound, Highland General Hospital, Alameda Health System
Dr. Nagdev is director of emergency ultrasound at Highland Hospital and assistant clinical professor (volunteer) of emergency medicine at the University of California, San Francisco.
References
- Bunting L, Kuper K. Bedside washout of a septic shoulder in the emergency department: a case report. Ann Emerg Med. 2016 Feb 10 [Epub ahead of print].
- Carpenter CR, Schuur JD, Everett WW, et al. Evidence-based diagnostics: adult septic arthritis. Acad Emerg Med. 2011;18(8):781-796.
- Patel DN, Nayyar S, Hasan S, et al. Comparison of ultrasound-guided versus blind glenohumeral injections: a cadaveric study. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2012;21(12):1664-1668.
- Zaia BE, Soskin PN. Images in emergency medicine. Man with severe shoulder pain. Gonococcal arthritis of the shoulder. Ann Emerg Med. 2014;63(5):528.
Pages: 1 2 3 | Single Page


No Responses to “Ultrasound-Guided Glenohumeral Joint Evaluation and Aspiration”