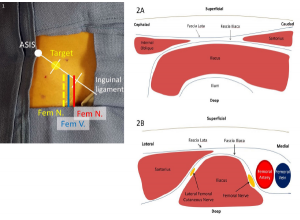
Figure 1. The inguinal ligament may be divided into thirds, with the target site for injection being the lateral one-third mark. This lies lateral to the femoral nerve and vasculature.
Figure 2. A: In the infrainguinal approach, the fascia lata and fascia iliaca form a “bow tie” when overlapping between the sartorius caudad and internal oblique cephalad, with underlying iliacus muscle spanning over the ilium. B: In the suprainguinal approach, the sartorius overlies the iliacus muscle on its lateral border, with the fascia iliaca separating the two muscles. The femoral nerve and vascular bundle lie medial to the iliacus muscle, and the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve lies between the muscle bodies.
Figure 1. The inguinal ligament may be divided into thirds, with the target site for injection being the lateral one-third mark. This lies lateral to the femoral nerve and vasculature. Figure 2. A: In the infrainguinal approach, the fascia lata and fascia iliaca form a “bow tie” when overlapping between the sartorius caudad and internal oblique cephalad, with underlying iliacus muscle spanning over the ilium. B: In the suprainguinal approach, the sartorius overlies the iliacus muscle on its lateral border, with the fascia iliaca separating the two muscles. The femoral nerve and vascular bundle lie medial to the iliacus muscle, and the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve lies between the muscle bodies.
By Joseph Harrington
|
on January 10, 2018
|
0 Comment


No Responses to “Figure 1. The inguinal ligament may be divided into thirds, with the target site for injection being the lateral one-third mark. This lies lateral to the femoral nerve and vasculature. Figure 2. A: In the infrainguinal approach, the fascia lata and fascia iliaca form a “bow tie” when overlapping between the sartorius caudad and internal oblique cephalad, with underlying iliacus muscle spanning over the ilium. B: In the suprainguinal approach, the sartorius overlies the iliacus muscle on its lateral border, with the fascia iliaca separating the two muscles. The femoral nerve and vascular bundle lie medial to the iliacus muscle, and the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve lies between the muscle bodies.”