
Why Do We Need Resuscitative TEE in the ED?
Echocardiography represents a valuable component in the evaluation of unstable patients, including those with undifferentiated shock and in cardiac arrest. In many settings, TTE guides resuscitations during the critical phase of care, can determine rapidly reversible causes, and can identify when efforts may be futile. Unfortunately, optimal views can be a challenge; recent data show that integrating TTE into cardiac arrests may inadvertently prolong compression pause duration.5 Some of the common factors limiting the quality of TTE images include body habitus and emphysema.
Explore This Issue
ACEP Now: Vol 39 – No 07 – July 2020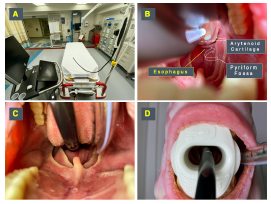
Figure 4: Probe insertion technique. (A) The TEE probe handle should be hung or held by an assistant to allow free movement of the shaft. (B) The probe should be inserted maintaining midline to avoid common sites of obstruction at the arytenoid cartilages and pyriform fossae. (C) Once at the base of the tongue at midline, a “chin lift” maneuver will facilitate passage by opening the esophagus. (D) Once in place, a bite block previously loaded into the probe should be placed to avoid damage by the teeth on the probe.
Felipe Teran
In our experience, we have found three primary applications where TEE can prove useful and influential in the emergency department.
- Guiding Cardiac Arrest Resuscitation: The primary indication for use of resuscitative TEE in the emergency department is during cardiac arrest.3,4 In addition to the same diagnostic and prognostic qualities provided by TTE images, including the identification of reversible causes such as cardiac tamponade or pulmonary embolism (PE), TEE also provides advantages during resuscitation. Recent animal and human data have shown that standard cardiac compressions may not squeeze the left ventricle but rather the left ventricular outflow tract. TEE allows rapid adjustment of the compression location and may result in higher rates of return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC).6 Also, chest compression interruptions can be limited because the probe can obtain optimal views of the heart during active CPR.7
- Evaluation and Management of Shock in Intubated Patients: Although TTE remains the first-line modality for the assessment of patients in shock in the emergency department, TEE is a powerful alternative for intubated patients in whom TTE windows are inadequate or unavailable. Once placed, TEE can help establish the etiology or predominant mechanism of shock, perform serial hemodynamic assessments estimating stroke volume (SV) and SV variation, determine preload sensitivity using respirophasic variation of superior vena cava diameter, and monitor hemodynamic interventions (ie, initiating or titrating vasopressor therapy).8–10
- Procedural Guidance: In addition to its diagnostic value and usefulness as a hemodynamic monitoring tool, resuscitative TEE has a unique role guiding several emergency procedures, such as initiation and monitoring ECMO, and the placement of intravenous pacemaker wires.11,12
TEE Safety
The risks associated with comprehensive TEE examinations have been studied extensively in the perioperative and echocardiography laboratory environments. Major complications such as oropharyngeal trauma, esophageal perforation, and major bleeding are exceedingly rare, with incidence rates ranging between 0.01 and 0.08 percent.13–16 Furthermore, in the resuscitative setting, the risk of these complications is often outweighed by the benefit of obtaining time-sensitive and lifesaving information, making the safety profile of TEE comparable to many other commonly performed emergency procedures.



No Responses to “How to Perform Resuscitative Transesophageal Echocardiography in the Emergency Department”