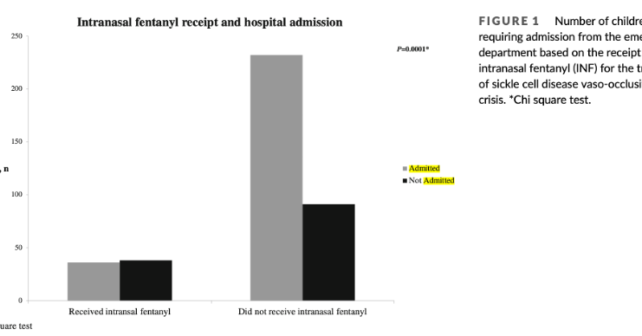
There was also a great deal of variation for admission rates which ranged from 45 to 90 percent. Despite this variation in practice, IN fentanyl administration was still associated with discharge even accounting for pain scores and opioid administration. Further, when the analysis includes only sites that administer IN fentanyl, the association is even stronger.
Explore This Issue
ACEP Now: Vol 42 – No 09 – September 2023The differences observed in this study make it uncertain if these findings can be generalized outside of these academic settings. However, adopting IN fentanyl administration does not seem difficult and community hospitals may want to consider this treatment option.
Bottom Line
Intranasal fentanyl may be helpful for children with SCD presenting with VOE.
Case Resolution:
You decide to give the patient a dose of IN fentanyl while she is awaiting IV access. After IV access is obtained, she receives a few doses of parenteral morphine and tells you that she feels like her pain is much better controlled. She is discharged from the ED.
Thank you to Dr. Dennis Ren for his help on this critical appraisal. He is a pediatric emergency medicine physician at Children’s National Hospital in Washington, DC.
Remember to be skeptical of anything you learn, even if you heard it on the Skeptics’ Guide to Emergency Medicine.
References
- Campbell F, Hudspith M, Choinière M, et al. An action plan for pain in Canada. Health Canada website. https://www.canada.ca/content/dam/hc-sc/documents/corporate/about-health-canada/public-engagement/external-advisory-bodies/canadian-pain-task-force/report-2021-rapport/report-rapport-2021-eng.pdf. Published May 2021. Accessed August 8, 2023.
- National Heart Lung, and Blood Institute. Evidence-based management of sickle cell disease: Expert panel report, 2014. National Institutes of Health website. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/evidence-based-management-sickle-cell-disease. Published 2014. Accessed August 8, 2023.
- Murphy A, O‘Sullivan R, Wakai A, et al. Intranasal fentanyl for the management of acute pain in children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;2014(10):CD009942.
- Murphy A, O‘Sullivan R, Wakai A, et al. Intranasal fentanyl for the management of acute pain in children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;2014(10):CD009942.
Pages: 1 2 3 | Single Page




No Responses to “Intranasal Fentanyl for Sickle Cell Vaso-Occlusive Pain”