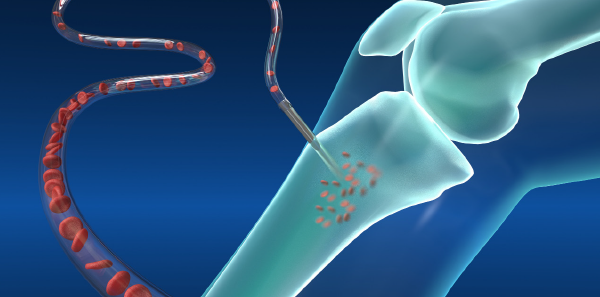
 Dr. Sampson is director of education, director of clinical research, and assistant medical director of MU Emergency Medical Services and associate clinical professor in the department of emergency medicine at the University of Missouri–Columbia.
Dr. Sampson is director of education, director of clinical research, and assistant medical director of MU Emergency Medical Services and associate clinical professor in the department of emergency medicine at the University of Missouri–Columbia.
Explore This Issue
ACEP Now: Vol 40 – No 01 – January 2021References
- Foëx BA. Discovery of the intraosseous route for fluid administration. J Accid Emerg Med. 2000;17(2):136-137.
- Rosenberg H, Cheung WJ. Intraosseous access. CMAJ. 2013;185(5):E238.
- Schindler P, Helfen A, Wildgruber M, et al. Intraosseous contrast administration for emergency computed tomography: a case-control study. PLoS One. 2019;14(5):e0217629.
- Barnard EBG, Moy RJ, Kehoe AD, et al. Rapid sequence induction of anaesthesia via the intraosseous route: a prospective observational study. Emerg Med J. 2015;32(6):449-452.
- Tan BKK, Chong S, Koh ZX, et al. EZ-IO in the ED: an observational, prospective study comparing flow rates with proximal and distal tibia intraosseous access in adults. Am J Emerg Med. 2012;30(8):1602-1606.
- Reddick AD, Ronald J, Morrison WG. Intravenous fluid resuscitation: was Poiseuille right? Emerg Med J. 2011;28(3):201-202.
- Reades R, Studnek JR, Vandeventer S, et al. Intraosseous versus intravenous vascular access during out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: a randomized controlled trial. Ann Emerg Med. 2011;58(6):509-516.
- Leidel BA, Kirchhoff C, Bogner V, et al. Comparison of intraosseous versus central venous vascular access in adults under resuscitation in the emergency department with inaccessible peripheral veins. Resuscitation. 2012;83(1):40-45.
- Rosetti VA, Thompson BM, Miller J, et al. Intraosseous infusion: an alternative route of pediatric intravascular access. Ann Emerg Med. 1985;14(9):885-888.
- EZ-IO intraosseus vascular access. Teleflex website. Accessed Dec. 11, 2020.
Pages: 1 2 | Single Page



2 Responses to “Intraosseous Myths: What ED Docs Should Know About this IV Alternative”
February 7, 2021
David A. Miramontes MD FACEP FAEMSYou forgot to mention the BEST IO site. THE DISTAL FEMUR in adults and peds. Better flow rates and can do cut down for obese patients with Yellow needle.
Though NOT “FDA approved” we use it extensively in EMS at San Antonio Fire Department and even infuse Whole Blood with no problem.
February 26, 2021
Stephen HoffmanThis IO article was very good. (My mentor at SF General Hospital was the doc who reincarnated the IO in the U.S., and pediatric EM in general, back in the ’80s.)
One caveat, though, about meds that can be used by the IO route: I agree that virtually everything CAN be used, but, from personal experience, I can tell you one drug that doesn’t work via IO. My patient was a 4-day old, who was brought in for fussiness and poor feeding. He had a regular and fixed HR of almost 300, narrow-complex. Dx: SVT. His color, sat., tone and CR were good, so we had time. We in the ED could not get in an IV, and after nearly 90 minutes, we finally put in an IO, in order to give adenosine. It did not work after multiple tries. The reason became obvious after thinking about it: the action of adenosine depends on getting the highest possible “instantaneous” concentration of the drug into the AV node, at one moment in time. This is why IV location (high up) and timing of the push and follow-up saline push are so important to success.
When this became obvious to us, we finally got smart and called up to the NICU, to ask a nurse to come down to the ED and help us start an IV. She did, got an IV in minutes, and we repeated the original dose of adenosine, but this time IV. Within seconds, the child was cardioverted to NSR, did very well, and went up to NICU for observation.
The take-home lesson was that whereas virtually every other drug, fluid, or blood product can be given IO, in the case of adenosine, (which has a unique mode of action, and depends on the highest possible “instantaneous” level of the drug in the AV node), you cannot achieve that peak level with the kinetics of adsorption from the marrow space into the circulation (IO route).
— Stephen Hoffman, MD