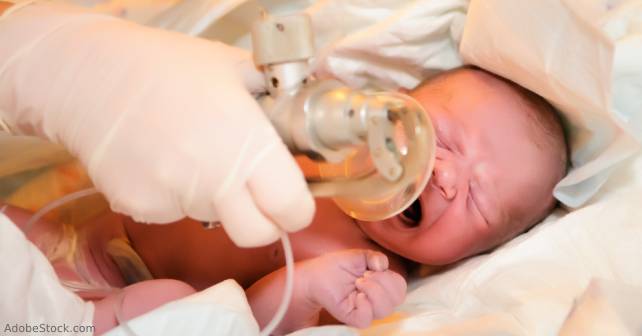
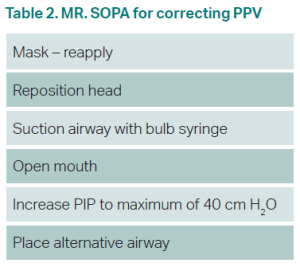
One team member should auscultate HR during the first 15 seconds of PPV. A rising HR is the best indication of effective PPV.3 If there is no increase in HR, PPV may be corrected with the MR. SOPA pneumonic (Table 2).
Explore This Issue
ACEP Now: Vol 43 – No 11 – November 2024After 30 seconds of effective PPV, the patient should be reassessed. If HR is 60–99, the MR. SOPA algorithm should be repeated for proper PPV.1 If HR is below 60, chest compressions should be started and an ECG placed.3 The two-hand technique is the most effective. Compressions should be delivered at a ratio of three compressions to one ventilation, for 90 compressions and 30 inflations in one minute.3 Vascular access through an umbilical vein catheter (UVC) should be obtained, although intraosseous (IO) access is acceptable.3
The patient should have an endotracheal (ET) tube placed. ET tube size should be 2.5 mm for neonates under 1,000 grams, 3.0 mm for 1,000–2,000 grams, and 3.5 for neonates over 2,000 grams.1 ET depth is generally “6 + the weight in kilograms,” so a three kg infant would have an ET tube be nine cm at the lip.1 Intubation is difficult; a laryngeal mask airway (LMA) is a useful alternative.2
If the patient is bradycardic after 60 seconds of compressions and ventilations, initiate medications. 0.01–0.03 mg/kg IV epinephrine, or 0.05–0.1 mg/kg through the ET tube, should be given every three to five minutes.3 Volume resuscitation with normal saline or blood may be given at 10 cc/kg over five to 10 minutes in infants with concerns for blood loss.3
In the post-resuscitative state, the patient should be transferred to a higher level of care, where they can be monitored for further complications and undergo therapeutic hypothermia.4 If all steps of resuscitation have been completed and HR remains undetectable 20 minutes after birth, goals of care should be discussed and termination of resuscitation considered.3
 Dr. Turner, originally trained at the Medical University of South Carolina, is an EM intern at Hershey Medical Center in Hershey, Pa.
Dr. Turner, originally trained at the Medical University of South Carolina, is an EM intern at Hershey Medical Center in Hershey, Pa.
 Dr. Sandelich is a pediatric emergency physician at Hershey Medical Center in Hershey, Pa.
Dr. Sandelich is a pediatric emergency physician at Hershey Medical Center in Hershey, Pa.
References
- Sawyer T, Umoren RA, Gray MM. Neonatal resuscitation: advances in training and practice. Adv Med Educ Pract. 2016;8:11-19.
- Garvey AA, Dempsey EM. Simulation in Neonatal Resuscitation. Front Pediatr. 2020;8:59.
- Aziz K, Lee HC, Escobedo MB, et al. Part 5: Neonatal Resuscitation: 2020 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care. Circulation. 2020;142(16_suppl_2):S524-S550.
- Raghuveer TS, Cox AJ. Neonatal resuscitation: an update. Am Fam Physician. 2011;83(8):911-918.
- Finster M, Wood M. The Apgar score has survived the test of time. Anesthesiology. 2005;102(4):855-857.
Pages: 1 2 3 | Single Page



No Responses to “Neonatal Resuscitation Tips”