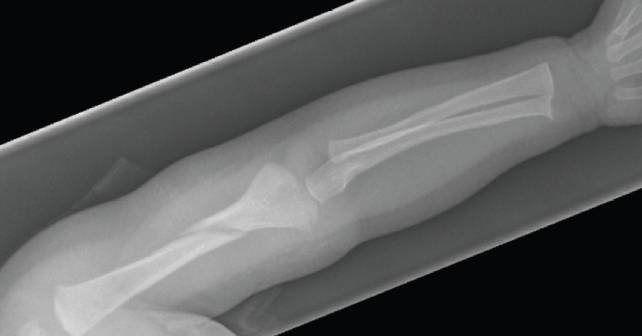
For children older than two years, with developmental delays who are suspected victims of NAT, skeletal survey should be strongly considered. For children between the ages of two and five years, the decision whether to get a skeletal survey should be based upon clinician judgement.
Explore This Issue
ACEP Now: Vol 43 – No 03 – March 2024
Skeletal surveys require considerable experience to obtain properly and to interpret accurately. Recommended imaging protocols are detailed by the American College of Radiology.3 If a severely injured child presents to a hospital without experience performing skeletal surveys and is awaiting transfer to a tertiary care center, it may be preferable to defer the survey until arrival at the receiving hospital. This should be discussed with the accepting physician.
Case Resolution
The patient was found to have a humeral fracture on X-ray. Subsequent skeletal survey revealed a healing ulnar fracture as well. The patient’s twin sibling also had a skeletal survey, which showed a healing ulnar fracture. A report was filed with Child Protective Services and the hospital’s child protection service was consulted. The hospital’s social worker was also notified.
 Dr. Rozzi is medical director of the forensic examiner team at WellSpan Health, and the secretary of ACEP’s Forensic Section.
Dr. Rozzi is medical director of the forensic examiner team at WellSpan Health, and the secretary of ACEP’s Forensic Section.
.
 Dr. Riviello is chair and professor of emergency medicine at the University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio.
Dr. Riviello is chair and professor of emergency medicine at the University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio.
References
- American Academy of Pediatrics, Section on Radiology. Diagnostic Imaging of Child Abuse. Pediatrics. 2009;123(5):1430–5.
- Botash AS, Ashraf I. CHAMP practice recommendation: Skeletal survey. CHAMP website. Published March 2021. Accessed February 28, 2024.
- ACR-SPR practice parameter for the performance and interpretation of skeletal surveys in children (ACR Res. 37). ACR website. Revised 2021. Accessed February 28, 2024.
Pages: 1 2 | Single Page




No Responses to “Scan for These Potential Signs of Non-Accidental Trauma”