Explore This Issue
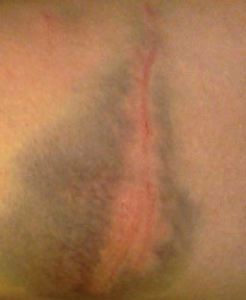
ACEP Now: Vol 36 – No 02 – February 2017Figure 1 (Left): Suboptimal quality photograph of an injury from a domestic violence assault.
The Case: You are called to testify in court for a domestic violence assault case. You saw the patient three years ago; she had sustained multiple bodily injuries. In addition to providing medical care, you took photographs of her injuries. While on the stand, you are shown the picture in Figure 1 and are asked to describe the location and size of the wound. How would you answer that question?
Discussion
In the case, the photograph does not allow the viewer to accurately know which body part is being depicted. Also, the size cannot be described. Photography has become an important documentation tool for injuries. It is used in documenting child abuse, elder abuse, domestic violence, sexual violence, and assault cases. In some departments, forensic nurse examiners (FNEs) are called upon to take photographs and document the findings. However, a FNE may not always be available, requiring the emergency provider to take the pictures. A few helpful hints will allow you to take photographs that actually represent the finding you identified.
Forensic photography supplements the medical forensic history and physical findings. It allows the viewer to see the injuries that the provider saw at the time of evaluation. The advent of digital photography has had a great impact on forensic photography. Several advantages of digital image capture include instant review of photo for quality and composition, no need for film or film development, and ease of storing and transfer of images. Prior to taking photos, there should be a department policy addressing the use of photographs. The policy should cover topics including consent, secure storage of images, and transfer of images. Risk management, information technology, and the medical records departments should be involved in policy development.
Patients should consent to have their photographs taken. A separate photographic consent form should be used. Patient have the right to refuse image capture of certain injuries or body parts. Also, the consent should address the release of images to law enforcement and/or district attorney’s offices. Images should be stored on a secure server and/or within the electronic health record.
The medical record should reflect that photographs were taken as well as the number taken and how they were stored. Transferring the images to a CD-ROM and storing the CD with the medical record or in a separate secure location or using a separate memory card for each patient are acceptable. Photographs depicting genitalia should be stored with particular sensitivity.
Some Photographic Tips
Equipment: Expensive equipment is not necessary. A good-quality point-and-shoot camera takes sufficient images. The camera should capture images of at least six megapixels and have macro lens capabilities. Macro lenses allow close-up shots and are represented by the “tulip” icon on most cameras. A built-in or separate flash is also required. Other essentials include spare batteries, media cards, computer cable, reference scales for measuring length, cleaning supplies, and the camera manual. A tripod or monopod may also be helpful.
Pages: 1 2 | Single Page






No Responses to “Tips for Taking Forensic Photographic Evidence in the Emergency Department”