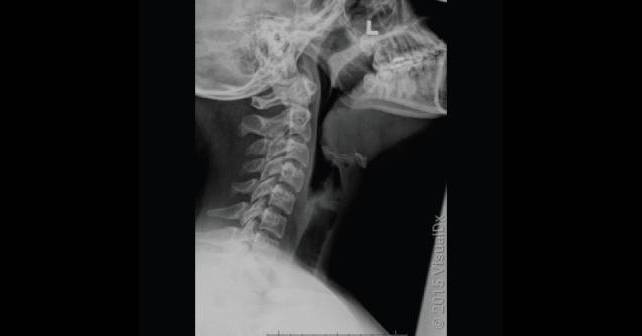
Answer: The correct answer is a) Epiglottitis
Explore This Issue
ACEP Now: Vol 43 – No 05 – May 2024Epiglottitis is a potentially life-threatening inflammation of the epiglottis and supraglottic space caused by infection (e.g., Haemophilus influenzae type b [Hib]) or injury (e.g., foreign body, caustic substance, thermal damage). As the epiglottis swells, it can cause airway obstruction and create a medical emergency. Presenting symptoms include high fever, sore throat, difficulty swallowing, dyspnea, hoarseness, stridor, tachycardia, drooling, and hot potato voice or dysphonia.
Protection of the airway is a priority, and treatment may require placement of an artificial airway, intravenous steroids, antimicrobial therapy to control infection, and surveillance in an intensive care unit. Tracheostomy may be required in severe cases if airway management is not achievable with medical intervention or oral/nasal intubation.
The leading cause of epiglottitis in children is bacterial infection. Hib remains a leading causal organism but has a markedly decreased incidence. Group A Streptococcus, Staphylococcus aureus, and H influenza types A and F, and non-typeable H influenza, in addition to viral and fungal infections, have all been associated with epiglottitis.
Since widespread immunization against Hib, the average age of epiglottitis in children has increased. Nonimmunized populations and immunocompromised individuals are at increased risk for epiglottitis.
Epiglottitis in adults is also primarily attributed to infection but from different organisms. Streptococcus pneumoniae is the leading infectious agent, with other viral, bacterial, and fungal sources described as causal agents.
(See the original question here.)
Reference
- Winter MW, Bryson PC. Epiglottitis. VisualDX.com website. Accessed April 1, 2024.




No Responses to “Visual Dx Answer: a) Epiglottitis”